Array reduce() 메소드
-> https://snupi.tistory.com/151
[Javascript][ES5] Array reduce()
Array map(), filter(), forEach(), includes(), push() 메소드 -> https://snupi.tistory.com/144 [Javascript][ES5] Array map() / filter() / forEach() / includes() / push() Array map() map() 메서드는 배..
snupi.tistory.com
Array.from(obj)
array-like object 에 array 메소드를 사용하려면,
Array.from(obj) 을 사용한다
이는 array-like object (NodeList, HTMLCollection, ... 등등) 을 array로 변환해준다
Array map()
map() 메서드는 배열의 모든 아이템에 대하여 function을 실행하는 메소드이다.
그리고 나서 function의 결과 값으로 새로운 배열을 만든다.
const alphabets = ["a", "b", "c"];
const showingA = alphabets.map(al => `A${al}`);
const showingIdx = alphabets.map((al, index) => `#${index} ${al}`);
console.log(showingA);
console.log(showingIdx);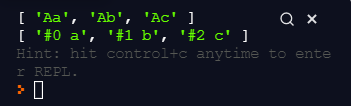
showingA)
alphabets 배열의 각각의 알파벳 string에 대하여
백틱으로 "A"를 붙여 배열로 반환한다.
showingIdx)
map() 함수에서는 idx 인자를 전달할 수 있다.
각각의 알파벳 string 앞에 #과 idx값을 붙여 배열로 반환한다.
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/map
Array sort()
sort() 메서드는 배열의 요소를 적절한 위치에 정렬한 후 그 원배열을 반환한다
기본 정렬 순서는 문자열의 유니코드 코드 포인트를 따른다
const months = ['March', 'Jan', 'Feb', 'Dec'];
months.sort();
console.log(months);
// ["Dec", "Feb", "Jan", "March"]
const array1 = [1, 30, 4, 21, 100000];
array1.sort();
console.log(array1);
// [1, 100000, 21, 30, 4]
또한 다음과 같이 compareFunction으로 정렬 순서를 정의할 수 있다
- compareFunction(a, b)의 return 값이 음수
- a - b ( a가 먼저 )
- compareFunction(a, b)의 return 값 === 0
- 변경하지 않고, 다른 요소에 대해 정렬
- compareFunction(a, b)의 return 값이 양수
- b - a ( b가 먼저 )
따라서 다음과 같이 오름차순을 정의할 수 있다 ( return a - b )
coins
.sort((first, second) => first.rank - second.rank)
.map(coin => <Coin key={coin.id} {...coin} />)
// coin 객체 배열을 오름차순으로 정렬한 뒤, map()으로 출력한다
Array filter()
filter() 메소드는 배열의 모든 아이템을 살펴보고,
function return이 true이면 배열에 넣는다.
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const result1 = words.filter(word => word.length < 6);
// ===
const testCondition = word => word.length < 6;
const result2 = words.filter(testCondition);
console.log(result1);
console.log(result2);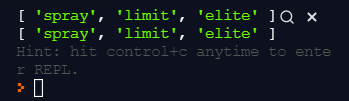
위와 같이 words 배열의 각 단어 string에 대하여
length가 6보다 작은지 확인하고, true면 배열에 넣어 반환한다.
Array forEach()
arr.forEach(current item [, current index [, current array] ])
forEach() 메소드는 각각의 아이템에 대해 어떤 시행을 한다.
이는 map(), filter()와는 달리 배열을 return 하는 것이 아니다.
const alphabets = ["a", "b", "c"];
alphabets.forEach(al => console.log(al));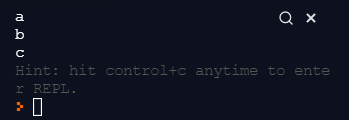
위 map()과 filter() 메소드는 배열로 반환하는 데에 반해,
foreach()는 각각 아이템에 대해 시행만 한다.
for of
forEach() 루프는 배열에서만 사용이 가능하고, 중간에 멈출 수 없지만
for of 루프는 어느 iterable 한 것에서든지 동작한다 (Array, Object, String, NodeList, ...)
for(const letter of "HELLOOOOOOOOOOOOOO") {
if(letter === "O")
break;
else
console.log(letter);
}
Array includes(), push(), shift(), unshift()
includes()는 해당하는 아이템이 배열에 존재하는지 확인할 수 있는 간단한 메소드이다.
push()는 아이템을 배열에 추가한다. (맨 뒤)
shift()는 큐에서 "pop"과 같은 동작을 하며 삭제된 요소가 반환된다
unshift는 덱에서 "front_push"와 같은 동작을 하며 배열의 새로운 길이가 반환된다
const alphabets = ["a", "c"];
if(!alphabets.includes("b")) {
alphabets.push("b");
}
console.log(alphabets);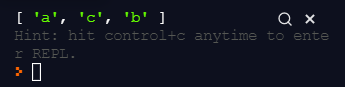
Array findIndex() / fill()
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/findIndex
Array.prototype.findIndex() - JavaScript | MDN
findIndex() 메서드는 주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 배열의 첫 번째 요소에 대한 인덱스를 반환합니다. 만족하는 요소가 없으면 -1을 반환합니다.
developer.mozilla.org
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/fill
Array.prototype.fill() - JavaScript | MDN
fill() 메서드는 배열의 시작 인덱스부터 끝 인덱스의 이전까지 정적인 값 하나로 채웁니다.
developer.mozilla.org
Array flat()
다차원의 배열의 차원 뎁스를 낮춰준다
const nums = [1, [2, [3, [4, [5]] ] ] ];
nums.flat(5);
// default depth === 1;'JS, TS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Javascript][ES6] Array Swapping, Omitting (0) | 2021.09.03 |
|---|---|
| [Javascript][ES6] 객체 구조 분해 할당 (Object Destructuring) / 전개 구문 (Spread Operator) / Rest parameter (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| [실습][Javascript] To Do List 만들기 (Nomad Coders) (0) | 2021.08.07 |
| [Javascript] 옵셔널 체이닝 (Optional chaining; ?.) 으로 다중 체크하기 / ?? 연산자 (0) | 2021.07.24 |
| [Javascript] JS 자료형변환 (to String / to Number / to Boolean) (1) | 2021.07.21 |

